題目:
魔術三角形是一個由1到9的數字所形成之三角形,
每邊由4個數字組成,邊與邊之間會有1個數字共用,而且每個邊
4個數字相加之總和是一樣的,舉例來說,下圖是一個魔術三角形,三個邊的數字和均為19。
我們以三角形最上面的數字7為起點,順時針方向列出所有9個數字來表示這個三角形,
表示為"781359264"
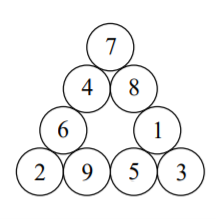 (取自108年彰雲嘉資訊科能力競試上午場P5)
(取自108年彰雲嘉資訊科能力競試上午場P5)
預先將下圖的三個藍色粗框部分填入數字,請填入其餘數字使其成為一個魔術三角形。
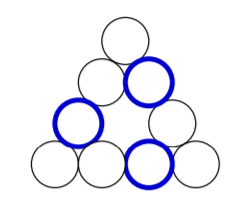 (取自108年彰雲嘉資訊科能力競試上午場P5)
(取自108年彰雲嘉資訊科能力競試上午場P5)
輸入:
三個1~9之間的數代表依順時針填入藍色粗框的3個數字。
輸出:
將形成的魔術三角形之9個數字合併成一個十進位數字輸出,若存在多個答案
,則輸出十進位數字最小者。若無法形成魔術三角形,則輸出1個0。
4 3 6
4 6 7
Ex 1 Output:
542937168
Ex 2 Output:
249561873
題解:
題目沒給時間限制,當然直接暴力做下去啊!
時間複雜度也只有O(6!) = O(720),
所以也不會超過1秒
可使用next_permutation()這個函式,
他是用來枚舉排列的工具,既然是排列,
有學過排列組合都知道不重複排列數是P(n,n)
那時間複雜度就會是O(P(n,n))=O(n!)
如果遇到排列數很多的就還是別用了吧
記得在用這個函式時要先把要排的數組先排序好,
才能完整枚舉所有排列。
上程式碼:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
| #pragma GCC optimize("Ofast")
#pragma loop_opt(on)
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
template<class T> long long Mod(T a,T b){return ((a%b)+b)%b;}
#define endl '\n'
#define ll long long
#define IO ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0);
#define GETOUT cout.tie(0);
#define gc getchar()
#define cendl cout << endl;
#define fr(bob,n,l) for(int bob=(n);bob<(l);++bob)
#define fra(ns,a) for(auto (ns):a)
#define frc(bot,ns,l) for(int bot=(ns);bot<=(l);++bot)
#define frx(i,ns,l) for(int i=(ns);i<(l);++i)
const int MAX=1e9+7;
const int MOD=998244353;
inline int nextint(){
int x=0,w=1;char ch=0;
while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){
if(ch == '-')w=-1;
ch=getchar();
}
while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9')x=x*10+(ch-'0'),ch=getchar();
return x*w;
}
int a[3];
vector<int> s;
inline void solve(){
cin >> a[0] >> a[1] >> a[2];
for(int i=1;i<=9;++i){
if(i!=a[0]&&i!=a[1]&&i!=a[2]){
s.push_back(i);
}
}
sort(s.begin(),s.end());
vector<vector<int> > ans(1000);
int cnt=0;
do{
if(s[0]+a[0]+s[1]+s[2] == s[2]+a[1]+s[3]+s[4]
&& s[2]+a[1]+s[3]+s[4] == s[4]+a[2]+s[5]+s[0]){
++cnt;
for(int i=0;i<6;i++){
ans[cnt].push_back(s[i]);
}
}
}while(next_permutation(s.begin(),s.end()));
if(cnt!=0){
for(int i=1,j=0,k=0;i<=9;i++){
if(i!=2 && i != 5 && i!=8){
cout << ans[1][j++];
}
else{
cout << a[k++];
}
}
cendl;
}
else{
cout << 0 << endl;
}
}
signed main(){
IO;
GETOUT;
int t;
t=1;
while(t--)solve();
return 0;
}
|
 (取自108年彰雲嘉資訊科能力競試上午場P5)
(取自108年彰雲嘉資訊科能力競試上午場P5) (取自108年彰雲嘉資訊科能力競試上午場P5)
(取自108年彰雲嘉資訊科能力競試上午場P5)